
A Digital Surface Model (DSM) represents Earth's surface, including natural and artificial structures. It is widely used in urban planning, forestry, and telecommunications. By incorporating LiDAR, satellite imagery, and aerial photogrammetry, DSMs help in 3D city modeling and solar panel analysis. They provide valuable elevation data for infrastructure development.

DTM represents the bare-earth surface by filtering out vegetation and buildings, making it crucial for hydrological modeling and infrastructure planning. These models are widely used for flood mapping, road construction, and geological studies. DTMs offer accurate elevation data for land-use planning and environmental monitoring.
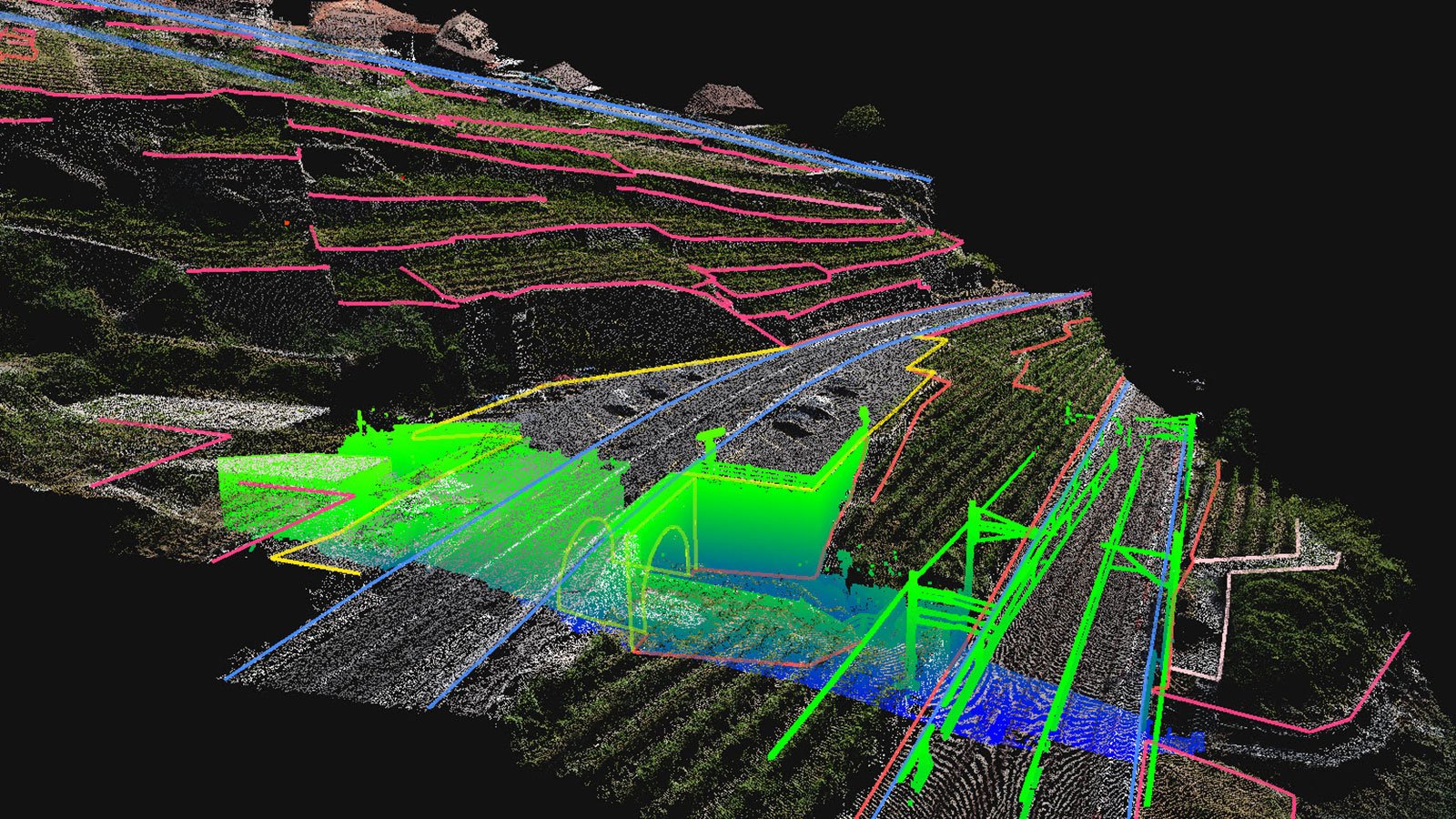
LiDAR-based DEMs provide high-precision elevation data using laser scanning technology. They are useful in forestry, archaeology, and environmental studies. With applications in coastline monitoring and flood risk assessment, LiDAR-generated models ensure accurate terrain representation even in dense vegetation.

Satellite-based DEMs, such as SRTM and ASTER, provide global topographic data for mapping and military applications. These models assist in climate research, disaster management, and glacier monitoring. They help analyze elevation changes across vast landscapes efficiently.